In the picture below shows an example in the specification demultiplexer using TTL IC 74HC237
-
This is default featured slide 1 title
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
-

This is default featured slide 2 title
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
-

This is default featured slide 3 title
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
-

This is default featured slide 4 title
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
-

This is default featured slide 5 title
Go to Blogger edit html and find these sentences.Now replace these sentences with your own descriptions.This theme is Bloggerized by Lasantha Bandara - Premiumbloggertemplates.com.
Demutiplex
In the picture below shows an example in the specification demultiplexer using TTL IC 74HC237
3 Bit to 8 Line Demultiplexer (Dekoder)
In the picture below shows an example in the specification demultiplexer using TTL IC 74HC237
The 74HC237 is a 3-to-8 line demultiplexer with latches at the three address inputs The 74HC237 essentially combines the 3-to-8 decoder function with a 3-bit storage latch. When the latch is enabled (LE = LOW), the 74HC237 acts as a 3-to-8 active LOW decoder. When the latch enable (LE) goes from LOW-to-HIGH, the last data present at the inputs before this transition, is stored in the latches. Further address changes are ignored as long as LE remains HIGH.
The output enable input (E1 and E2) controls the state of the outputs independent of the address inputs or latch operation. All outputs are HIGH unless E1 is LOW and E2 is HIGH.
Quick reference data demultiplexer 74HC237
- supply voltage: 0.5 +7 V
- input diode current: ±20 mA
- output diode current: ±20 mA
- output source or sink current: ±25 mA
- storage temperature: 65 +150 °C
- power dissipation: 750 mW
Decoder 4 Bit to 16 Line
- Supply Voltage: 0.5 to + 18 V
- Input Voltage: 0.5 to VDD + 0.5 V
- Total Power Dissipation (per package): 100 mW
- Operating Temperature : 40 to + 85 C
- Storage Temperature – 65 to + 150 C
Stresses above those listed under ”Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections
Transformasi Sumber
Not any source can be transformed. A voltage source in series with the new resistans can be transformed into a source of flow in parallel with resistans. Instead of a flow in parallel with the resistans transformation can be a source of voltage in series with the resistans. In general, how to change the power source into a source of other types shown in the picture below:

- Example


- Example 2


The results shown in the picture below:

Analisis Node/Simpul/Titik Rangkaian Elektronika
- Determine the amount of twist in the series.
- Choose a Simpul reference mark and the rest with a certain voltage, such as V1, V2, V3 and so on.
- Determine the direction of flow on each knot. On a note that is not the directions, the directions are usually chosen exit / leave the simpul. Rename the current I1, i2, I3, and so on.
- Apply Kirchoff current law at every twist in the simpul, except reference. Consider that all flows that do not know the directions, will leave every simpul.
- Complete equality of linear simultan
Expressed in the form of a matrix:
Hukum OHM
States that "the voltage across the various types of materials are proportionate with the straight flow of the stream." Mathematically expressed by:

Ohm's law formula can be derived as follows:

V is the voltage (in volt), I is the current that flows (in ampere) and R is resistansi or obstacles (in ohm, Ω) which is 1 ohm value is equal to 1 volt / ampere.
Resistansi is a measure of how large flow by preventing elements. Reverse of resistansi (1 / Ω, S) is called with konduktansi (G). Konduktansi is a measure of how good flowing currents akan allowed in the series. The mathematical relationship between resistansi and konduktansi stated with
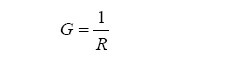
Answer:

Answer:

Hukum Kirchoff Arus - Kirchoff tegangan
States that "all the algebraic number of the flow enters a knot / point in the series is a zero" or "the amount of flow that enters the knot in a series with the same amount of flow that is out of the knot."
Expressed mathematically with
As an illustration shown in the picture below:
So based on the law applicable kirchof flow:
-Hukum Kirchoff Tegangan
States that "the amount of voltage that all algebraic corral a road closed (loop) in a series of electricity is zero." Mathematically expressed by:
-Example Kirchoff Tegangan
Determine the voltage of the unknown in the following series!
Answer:
By applying Kirchoff voltage law is
Determine the flow of the unknown from the image below!
Answer:
By applying the law kirchoff flow on a point, it will be valid
By applying the law kirchoff flow at the point b, it will be valid
By applying the law kirchoff flow at the point c, it will be valid
Analisis Loop/Mesh pada Rangkian Elektronika
1. Determine the direction of flow in each loop in the series. Usually selected with the clockwise direction.
2. Determine the polarity of each element in the series.
a. In the source: cash flow from the polarity (-) to the polarity (+)
b. In the burden: cash flow from the polarity (+) to the polarity (-)
3. Apply Kirchoff Voltage Law in each loop is in series, so that equality of the number of the loop.
4. Complete the simultaneous equation.
Example :
Decide which is the current flowing in each loop of the following series! :
Answer:
specify the first flow direction in each loop. We select the direction of the finger so that it becomes a series:
By applying Kirchoff voltage law to each loop is
With substitution and eleminasi second loop equation is:
Simultans that equality can also be obtained by using matrix algebra with the first claim to the loop equation in the form of a matrix as follows:
Besaran Pokok dan Besaran Turunan
Besaran Pokok
Besaran pokok adalah besaran yang satuannya telah ditetapkan terlebih dahulu dan tidak diturunkan dari besaran lain.
Besaran pokok dalam Sistem Internasional
| Nama | Simbol dalam rumus | Simbol dimensi | Sat. Stand. Internas | Simbol satuan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panjang | l, x, r, dll. | [L] | meter | m |
| Waktu | t | [T] | detik (sek.) | s |
| Massa | m | [M] | kilogram | kg |
| Arus listrik | I, i | [I] | ampere | A |
| Suhu | T | [θ] | kelvin | K |
| Jml. molekul | n | [N] | Mol | mol |
| Intensitas cahaya | Iv | [J] | Kandela | Cd |
Panjang
Satuan panjang adalah "meter".
Massa
Massa zat merupakan kuantitas yang terkandung dalam suatu zat. Satuan massa adalah "kilogram" (disingkat kg)
Waktu
Satuan waktu adalah "sekon" (disingkat s) (detik)
Definisi :
Satu sekon adalah selang waktu yang diperlukan oleh atom sesium-133 untuk melakukan getaran sebanyak 9 192 631 770 kali dalam transisi antara dua tingkat energi di tingkat energi dasarnya (CGPM ke-13; 1967)
Kuat arus listrik
Satuan kuat arus listrik adalah "Ampere" (disingkat A)
Definisi :
Satu Ampere adalah kuat arus tetap yang jika dialirkan melalui dua buah kawat yang sejajar dan sangat panjang, dengan tebal yang dapat diabaikan dan diletakkan pada jarak pisah 1 meter dalam vakum, menghasilkan gaya 2 X 10-7 newton pada setiap meter kawat.
Suhu
Satuan suhu adalah "kelvin" (disingkat K)
Definisi
Satu Kelvin adalah 1/273,16 kali suhu termodinamika titik tripel air (CGPM ke-13, 1967).
Dengan demikian, suhu termodinamika titik tripel air adalah 273,16 K. Titik tripel air adalah suhu dimana air murni berada dalam keadaan seimbang dengan es dan uap jenuhnya.
Jumlah molekul
Satuan jumlah molekul adalah "mol".
Intensitas cahaya
Satuan intensitas cahaya adalah "kandela" (disingkat Cd).
Definisi :
Satu kandela adalah intensitas cahaya suatu sumber cahaya yang memancarkan radiasi monokromatik pada frekuensi 540 X 1012 hertz dengan intensitas radiasi sebesar 1/683 watt per steradian dalam arah tersebut (CGPM ke-16, 1979)
Besaran turunan
Besaran turunan adalah besaran yang didapat dari penggabungan besaran-besaran pokok.Contoh besaran turunan:
| Besaran | Satuan | Singkatan |
|---|---|---|
| Kecepatan | meter per sekon | m/s |
| Percepatan, percepatan gravitasi | meter per sekon kuadrat | m/s² |
| Luas | meter persegi | m² |
| Volume | meter kubik | m³ |
| Gaya, berat, tegangan tali | Newton (kilogram meter per sekon persegi) | kg m/s² |
| Debit | meter kubik per detik | m³/s |
| Energi, usaha | Joule | J |
| Rapat tenaga | joule per meter kubik | J/m³ |
| Tegangan permukaan, tetapan pegas | Newton per meter | N/m |
Satuan - Satuan Listrik dan Besaran Listrik
Satuan Satuan Listrik
- Joule (J)
Adalah satuan dasar untuk kerja atau energi yang didefinisikan sebagai 1 Newton-meter (1Nm). Penggunaan gaya 1 N yang konstan sepanjang jarak 1 meter akan mengeluarkan energi 1 Joule. 1 Joule adalah ekivalen dengan 0, 73756 kaki Pound Gaya (ft-lbf). Satuan Energi lainnya adalah Kalori (Cal), sama dengan 4,1868 Joule, Satuan Termal British (British Thermal Unit, Btu) yang besarnya sama dengan 1055,1 Joule dan KiloWatt-jam (KiloWatt-hour, KWh) sama dengan 3,6 X 106 Joule. - Watt (W)
Adalah banyaknya kerja yang dilakukan per satuan waktu. Satuan dasar daya adalah Watt (W) yang didefinisikan sebagai 1 Joule/second. 1 Watt adalah ekivalen dengan 0,7375 ft-lbf/s. Juga ekivalen dengan 1/745,7 daya kuda (Horse Power = HP). - Newton (N)
Adalah satuan dasar untuk gaya yang menyatakan gaya yang diperlukan untuk memberikan percepatan sebesar 1 meter per detik (1m / s2) kepada massa 1 kg. Gaya 1 Newton adalah ekivalen dengan 0,22481 Pound Gaya (lbf).
Besaran Listrik
- Muatan Listrik
Gaya listrik terdiri dari dua macam, yaitu :
1. Gaya listrik yang saling tarik-menarik (tidak sejenis)
2. Gaya listrik yang tolak-menolak (sejenis)
Semua materi terdiri dari bagian-bagian yang disebut dengan atom. Atom terdiri atas tiga macam partikel dasar, yaitu :
1. Elektron (Bermuatan listrik Negatif)
2. Proton (Bermuatan listrik Positif)
3. Neutron (tidak bermuatan listrik)
Massa dari ketiga partikel tersebut telah ditentukan secara ekperimental dan besarnya adalah 9,10956 x 10-31 kg untuk Elektron dan ± 1840 kali lebih besar untuk Proton dan Neutron.Satuan muatan dasar disebut dengan Coulomb Menurut Charles Coulomb : "Dua partikel kecil yang bermuatan identik dan berjarak satu meter dalam vakum dan tolak-menolak dengan gaya sebesar 10-7 c2 Newton mempunyai muatan yang persis identik, yang besarnya masing-masing ± satu Coulomb". - Arus
Muatan yang bergerak disebut dengan arus. Arus yang terdapat di dalam sebuah jalur tertentu, seperti misalnya kawat logam (tembaga), mempunyai besar dan arah yang diasosiasikan dengan adanya muatan bergerak melalui sebuah titik tertentu per satuan waktu dalam arah tertentu. Definisi umum dari arus sebagai perubahan muatan per satuan waktu, dq/dt. Simbol arus adalah I atau i,
maka : i = dq/dt ………. ampere (A)
Satuan dasar arus adalah ampere (A), yang menyatakan banyaknya muatan yang mengalir dengan laju 1 C/s. Kata ampere berasal dari nama seorang ilmuan dari Prancis, yaitu : A.M Ampere.
Adapun jenis-jenis arus, yaitu :
a. Arus Searah (Direct Current)
Adalah arus yang konstan (tetap).
b. Arus Bolak-balik (Alternating Current)
Adalah arus yang berubah menurut bentuk gelombang sinusoidal terhadap waktu (t).
c. Arus Eksponensial
Adalah arus yang berbentuk eksponensial.
d. Arus Sinus Teredam
Adalah arus yang berbentuk sinus teredam - Tegangan
Elemen rangkaian yang umum akan ditandai dengan sepasang titik ujung (terminal) yang dapat dihubungkan dengan elemenelemen rangkaian yang lain. Misalkan bahwa sebuah arus searah diarahkan ke titik ujung (terminal) A melalui elemen memerlukan pengeluaran energi.
Maka dikatakan terdapat tegangan listrik atau perbedaan potensial diantara kedua titik ujung tersebut, atau terdapat tegangan listrik atau selisih potensial "melintasi" elemen tersebut.
Secara khusus tegangan melintasi elemen didefinisikan sebagai kerja yang perlu untuk menggerakan muatan positif sebesar 1 C dari satu titik ujung melalui alat tersebut ke titik ujung yang lain. Satuan untuk tegangan adalah volt (V), yang sama dengan 1 Joule / Coulomb dan tegangan dinyatakan dengan simbol atau lambang V atau volt. Kata volt berasal dari nama seorang ilmuan Italia, yaitu : Allessandro Guiseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta. Tanda untuk tegangan dinyatakan dengan tanda aljabar plus (+) atau minus (-).
- Daya
Tegangan telah didefinisikan sebagai energi yang dibelanjakan dan daya adalah laju dengan energi dibelanjakan. Lambang atau simbol daya adalah P atau p. Jika satu joule energi diperlukan untuk memindahkan satu coulomb muatan per detik melalui alat adalah satu watt. Tenaga yang diserap ini haruslah sebanding dengan banyaknya coulomb yang dipindahkan per detik, atau arus, dan sebanding dengan energi yang diperlukan untuk memindahkan satu coulomb melalui elemen atau tegangan, atau watt. Jadi :
P = V. I ………. watt








 truth table IC 74HC237 demultiplexer
truth table IC 74HC237 demultiplexer
































